Anticodon of a Particular Trna Molecule is
In translation messenger RNA mRNA is decoded in a ribosome outside the nucleus to produce a specific amino acid chain. They are found in tRNAs and allow the tRNAs to bring the correct amino acid in line with an mRNA during protein production.
Modifications Of The Human Trna Anticodon Loop And Their Associations With Genetic Diseases Springerlink
The tRNA contains a three-letter code on one side and carries a specific amino acid on the other side.

. Recognizing the structure of the mRNA bound to a tRNA. During RNA process which structures are removed from the strand. Discuss the canonical role of tRNAs in mRNA translation.
What two structures are attached to the ends of the tRNA. Depending on the protein being built the next amino acid could be any one of the twenty. Transfer RNA serves as a link or adaptor between the messenger RNA mRNA molecule and the growing chain of amino acids that make up a protein.
Checking and decoding and start of handing over one amino acid molecule. A particular codon will always code for the same amino acid wherever it is found. Decipher the segment of mRNA for both the.
Each time an amino acid is added to the chain a specific tRNA pairs with its complementary sequence on. The transfer RNA tRNA is one type of RNA molecule. Preparation of uncharged tRNA for exit.
Transfer RNA abbreviated tRNA is a small RNA molecule that plays a key role in protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule. A segment of mRNA considered an exon in one molecule can be an intron in another.
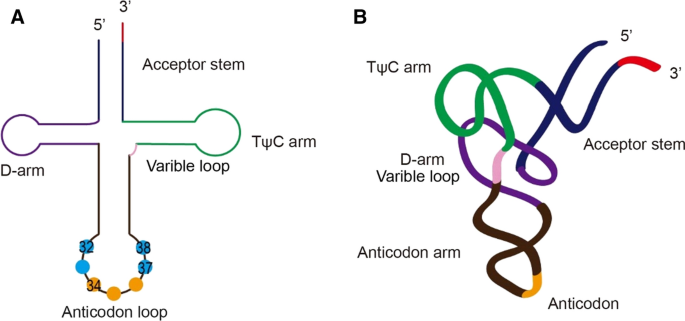
The incorporation of the correctly encoded amino acids into proteins depends on the attachment of each amino acid to an appropriate tRNA as well as on the specificity of codon-anticodon base pairing. A typical tRNA has bases numbering from 1-76 using the standard numbering convention where position 1 is the 5 end and 76 is the 3 end. These double stranded stems have complementary base pairs.
The amino acid is bonded to the tRNA molecule by enzymes in the cytoplasm. During this stage a small ribosome sub-unit links onto the start end of an mRNA strand. During the translation process the Anticodon bases form corresponding base sets among the bases of.
Science Biology QA Library A single base addition and a single base deletion approximately 15 bases apart in the mRNA specifying the protein lysozyme from the bacterial virus T4 caused a change in the protein from its wil-type compositionlys-ser-pro-ser-leu-asn-ala-ala-lysto the mutant form lys-val-his-his-leu-met-ala-alalys. During protein production amino acids are bound together into a string much like beads on a necklace. In molecular biology and genetics translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA to RNA in the cells nucleusThe entire process is called gene expression.
Transfer RNA tRNA is an adapter molecule that links a specific codon in mRNA with its corresponding amino acid during protein synthesis. The three-base sequence in a tRNA molecule that pairs with a complementary codon on mRNA is known as an _____. Common features of of yeast alanyl tRNA tRNA molecule Page 23 24.
This particular tRNA carries a methionine amino acid. If the fit is incorrect the tRNA is rejected and presumably other RNAs will continue to be tried until the correct one is found. Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products protein or non-coding RNA and ultimately affect a phenotype as the final effectThese products are often proteins but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA tRNA and small nuclear RNA snRNA the.
Several regions of the single stranded molecule form double stranded stems or arms and single stranded loops due to folding of various regions of the molecule. 3D structure of tRNA Page 24 25. Here Orellana et al.
A special RNA molecule that can bind to amino acids known as a transfer RNA or tRNA recognizes this sequence and binds to it. TRNA function and gene expression profiles are dynamically regulated by post-transcriptional tRNA modifications. TRNAs are enzymatically modified post-transcriptionally.
The attachment of amino acids to specific tRNAs is mediated by a group of enzymes called aminoacyl tRNA synthetases which were discovered by Paul Zamecnik and Mahlon. As the tRNA molecule returns with the amino acid the anticodon of the tRNA binds to the codon of the mRNA and moves through the ribosome. When the tRNA recognises its complementary codon in the mRNA strand it goes to collects its specific amino acid.
Its job is to carry the amino acid that matches the mRNA codon to the ribosome. Peptide synthesis consolidation elongation and transfer of peptide chain to site A. Anticodons are basically the section of a transfer RNA t RNA is a categorization of three bases which are corresponding to codons in the mRNA.
This is where the ribosome comes in. A transfer RNA molecule can enter the ribosome guaranteed to an organic compound. Its important that the.
Anticodons are sequences of nucleotides that are complementary to codons. TRNA with their associated aminoacids will enter the ribosomal site A and will be checked by a checking factor to see if there is a correct fit between the codon on the messengers RNA and the anticodon of tRNA. The code on tRNA called an anti-codon must match the three-letter code called a codon on the mRNA already in the ribosome.
Solved 21 The Anticodon Of A Particular Trna Molecule Is Complementary To The Corresponding Triplet In Rrna Complementary To The Corresponding Mrna Codon The Part Of Trna That Bonds To A Specific

Anticodon An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Comments
Post a Comment